Resources
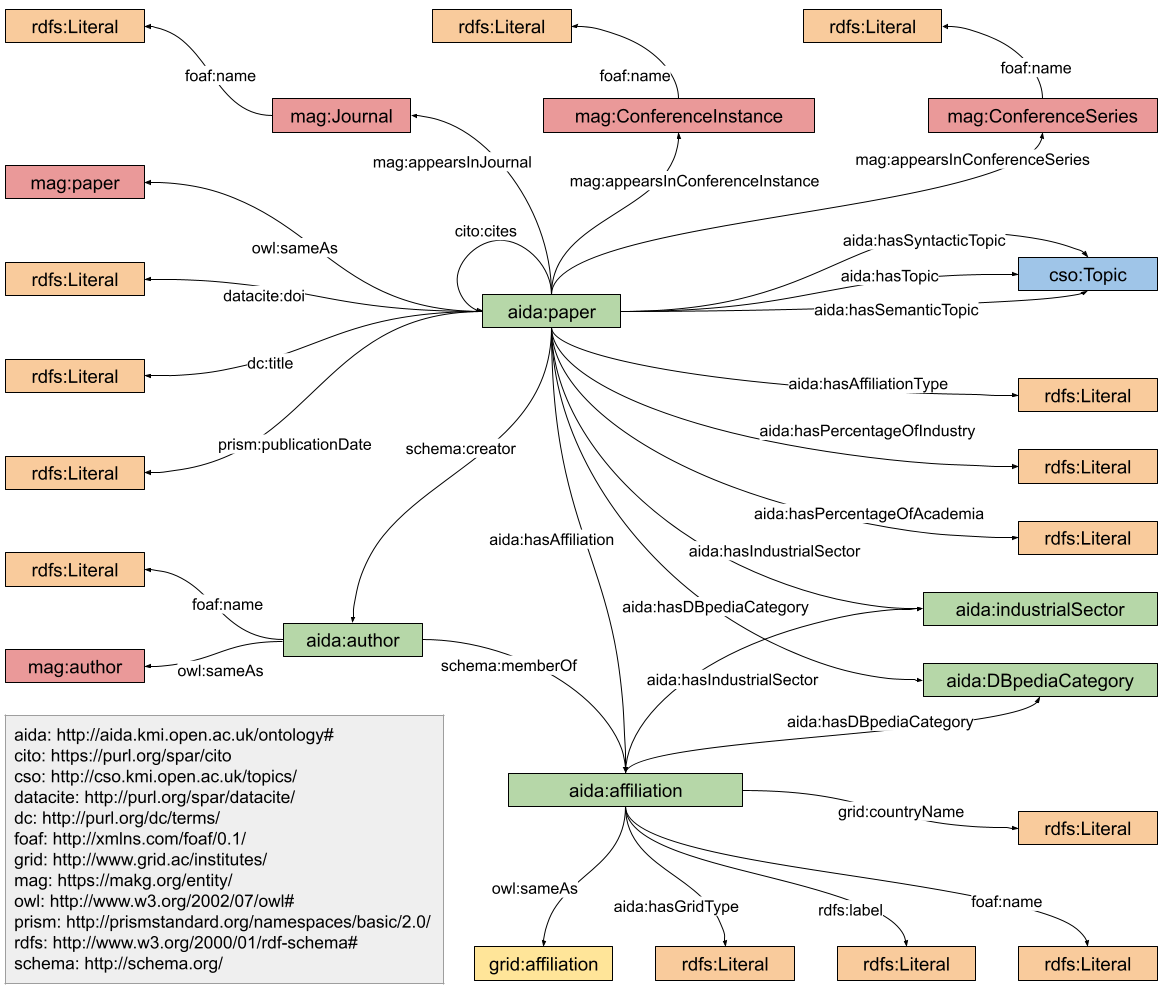
AIDA Data Model
The AIDA data model is based on AIDA Schema and nine additional relationships from Schema.org, RDFS, FOAF and others.
AIDA Schema
- hasSyntacticTopic, we use this relation to indicate the syntactic topics identified in a paper or a patent;
- hasSemanticTopic, we use this relation to indicate the semantic topics identified in a paper or a patent;
- hasTopic, we use this relation to indicate the topics identified in a paper or a patent (including syntactic and semantic);
- hasAffiliation, we use this relation to indicate the affiliation of a paper;
- hasAffiliationType, we use this relation to indicate the kind of affiliation of papers and patents: academia, industry, collaborative;
- hasAssigneeGridType, we use this relation to indicate the type of the assignee of a patent according to the GRID classification: Education, Company, Government, Non-profit and others;
- hasGridType: we use this relation to indicate the type of an affiliation according to the GRID classification: Education, Company, Government, Non-profit and others;
- hasPercentageOfAcademia, we use this relation to indicate the percentage of authors who authored this paper or patent, and belong to academia;
- hasPercentageOfIndustry, we use this relation to indicate the percentage of authors who authored this paper or patent, and belong to industry;
- hasIndustrialSector, we use this relation to indicate the industrial sector of an affiliation;
- isInDimensionsWithId, we use this relation to indicate the patent id used in Dimensions database;
- hasDBpediaCategory, we use this relation to indicate the industrial sector (DBpediaCategory) given by DBpedia in About:Property and About:Industry;
and six classes:
- paper, the class of papers;
- patent, the class of patents;
- author, the class of authors;
- affiliation, the class of both academic and industrial affiliations;
- industrialSector, the class of the industrial sectors;
- DBpediaCategory, this class is populated by all the categories that we inferred from DBpedia. As some of them are literals we created a class.
Additional relationships
- http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#type, we use this relationship to indicate if an entity is of type paper, patent, affiliation, or author;
- http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#label, we use this relationship to indicate the label of an affiliation;
- http://schema.org/creator, we use this relationship to indicate the author of a paper;
- http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl/sameAs, we use this relationship to connect papers, authors and affiliation to external knowledge graphs;
- http://purl.org/dc/terms/title, we use this relationship to indicate the title of paper entities;
- http://purl.org/spar/datacite/doi, we use this relationship to indicate the DOI of a paper;
- http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name, we use this relationship to state the name of an author and the affiliation;
- http://schema.org/memberOf, we use this relationship to indicate the affiliation of an author;
- http://schema.org/relatedLink, we use this relationship to state the related link of a patent.
- http://prismstandard.org/namespaces/basic/2.0/publicationDate, we use this relationship to state the year of publication of papers.
External entities
- cso:Topic, the topic from CSO;
- gp:patent, the patent from Google;
- grid:affiliation, the affiliation entity from GRID;
- mag:author, the author from Microsoft Academic Graph;
- mag:paper, the paper from Microsoft Academic Graph;
INDUstrial Sector Ontology (INDUSO)
The Industrial Sector Ontology (INDUSO) is a two-level taxonomy describing 66 industrial sectors.
INDUSO was created using a bottom-up method that took into consideration the large collection of publications and patents from MAG and Dimensions. Specifically, for each affiliation described in the documents with a GRID ID, we extracted from DBpedia the objects of the properties About:Purpose and About:Industry. We applied a bottom-up hierarchical clustering approach for merging similar sectors.
For instance, the industrial sector "Computing and IT" was derived from categories such as "Networking hardware", "Cloud Computing", and "IT service management".
Finally, we arranged the resulting sectors in a two-level taxonomy to have the first level sector including different second-level sectors. For example, the first level sector "energy" includes "nuclear power", "oil and gas industry", and "air conditioning".
Ontology
- http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core#broader, we use this relation to indicate when an industrial sector is broader than another;
- http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#wasDerivedFrom, we use this relation to indicate from which DBpedia categories such industrial sector was derived.
and every entity is an industrial sector from the AIDA Schema http://aida.kmi.open.ac.uk/ontology#industrialSector.